Prepare to be amazed by the groundbreaking research conducted by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. These brilliant minds have already revolutionized the treatment of COVID-19 by redesigning a hepatitis C drug. And now, they’re setting their sights on cancer.
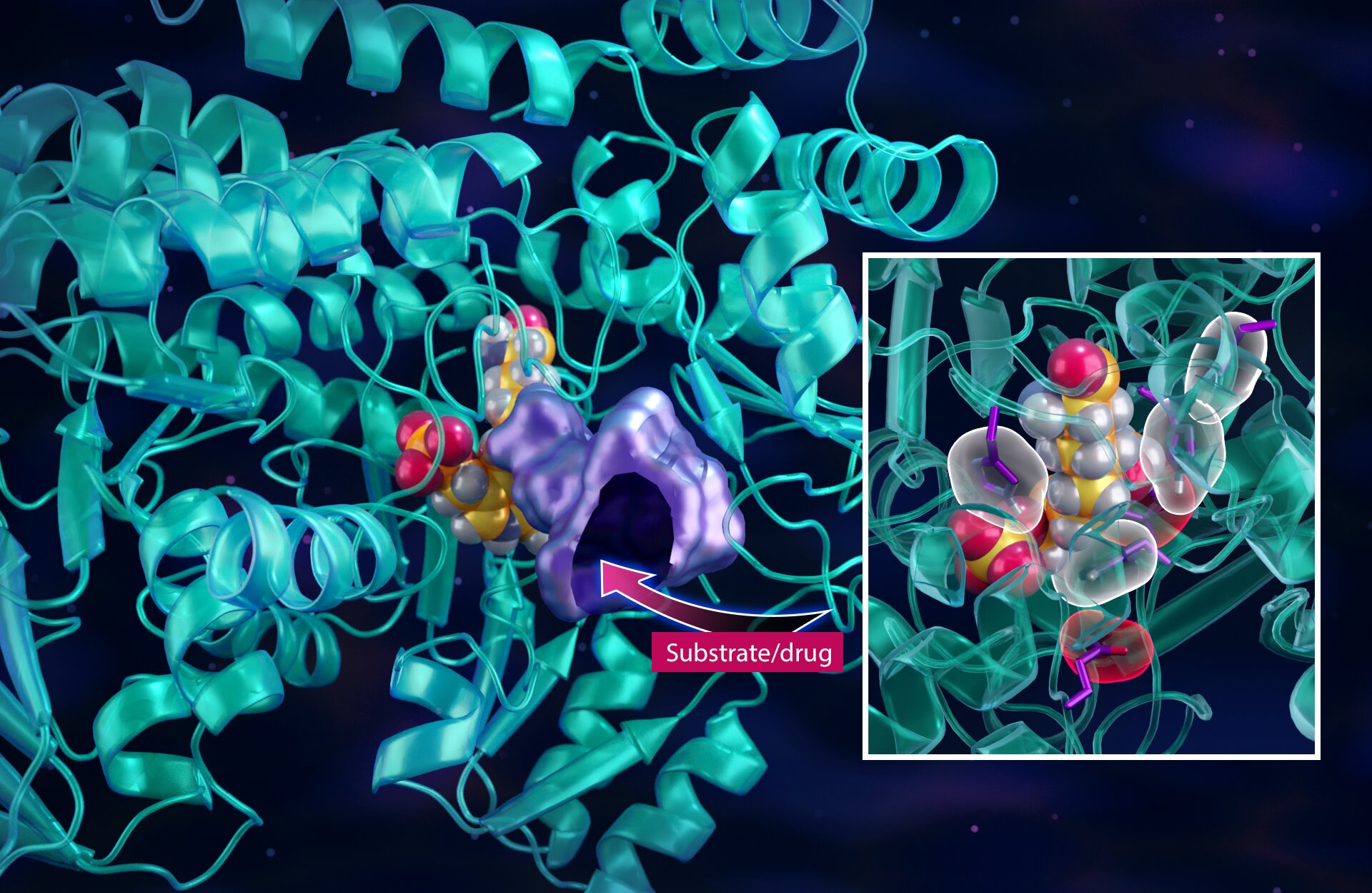
In their latest study, published in the journal Communications Chemistry, these brilliant scientists have used the power of neutrons and X-rays to unlock the secrets of cancer. They have mapped every atom, chemical bond, and electrical charge within a key enzyme that cancer cells rely on to reproduce.
This groundbreaking information opens up a world of possibilities for developing new drugs that can cut off the vital resources cancer cells need to thrive. Imagine a future where highly aggressive tumor-forming cancers like lung, colon, breast, pancreatic, and prostate cancers can be effectively treated.
Senior scientist Andrey Kovalevsky explains, “If we’re ever going to beat cancer, we need to explore every option and study every aspect of the disease. From tumors, cells, and molecules down to individual atoms.”
One specific pathway that has caught the attention of Kovalevsky and his team is the one-carbon metabolism pathway. This pathway plays a crucial role in synthesizing important biological molecules that cancer cells rely on for growth and multiplication. By targeting this pathway, the researchers hope to develop drugs that can starve cancer cells of their fuel sources.
But designing these drugs requires a deep understanding of the enzyme structure at the atomic level. That’s where the power of neutron and X-ray scattering experiments comes in. These experiments allow the scientists to map the location of every atom, chemical bond, and electrical charge within the enzyme structure.
By understanding how small molecules attach to the enzyme, the researchers can design drugs that fit perfectly, like puzzle pieces in 3D. It’s like finding the right battery to power specific electronic devices.
Neutrons, in particular, are crucial for studying light elements like hydrogen, which make up a significant portion of biological systems. Tracking hydrogen atoms helps the researchers understand the strength of chemical bonds between the drug molecules and the enzyme.
This research is just the beginning. The next steps involve studying the enzyme in different reaction stages and testing it against existing drug inhibitors. The goal is to develop a more effective treatment that reduces the rate of cancer progression.
So, get ready to witness the future of cancer treatment. These scientists are on the brink of a breakthrough that could change countless lives. Stay tuned for more updates!