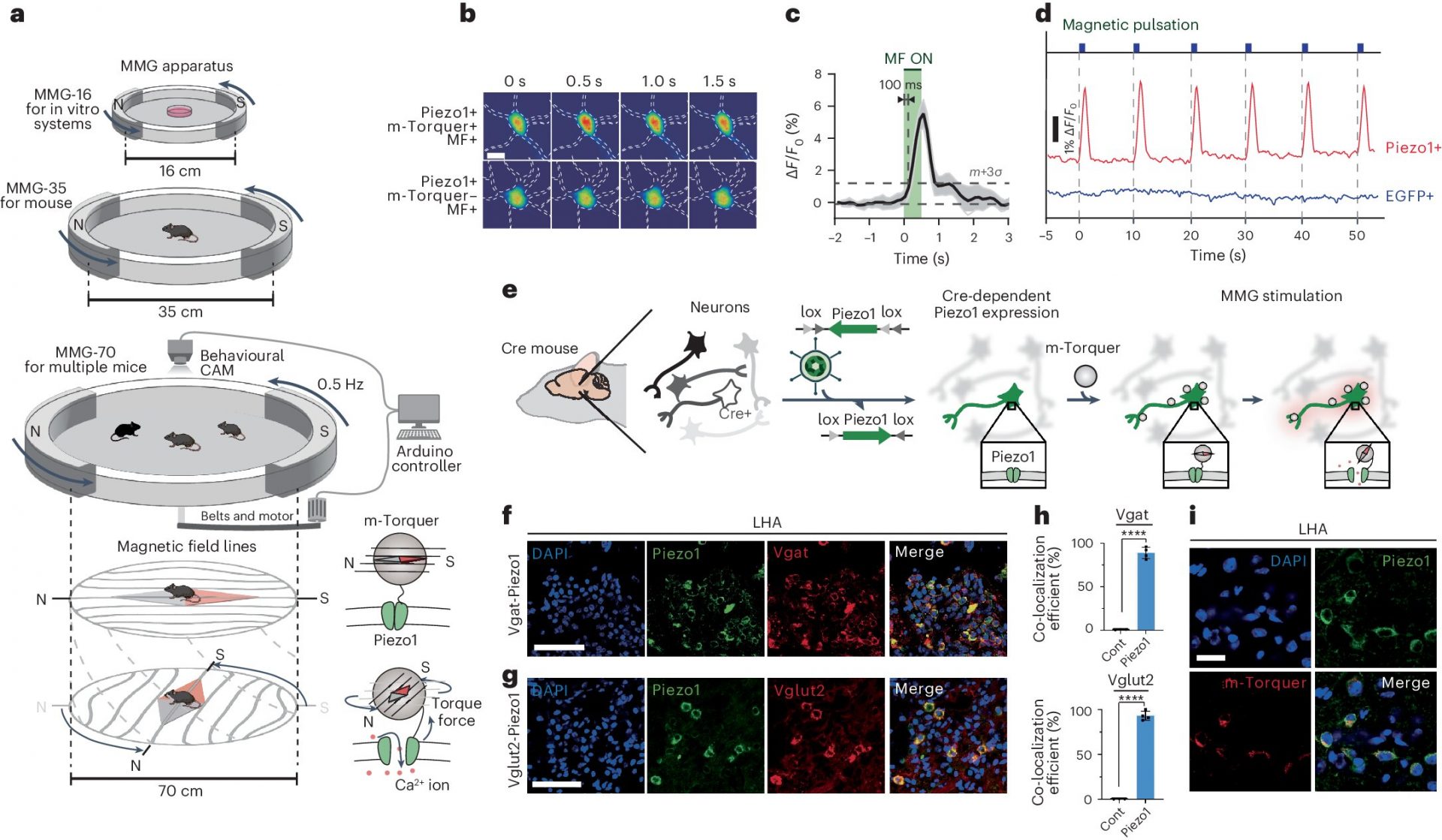
Researchers at the Center for Nanomedicine within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and Yonsei University in South Korea have unveiled a groundbreaking technology that can manipulate specific regions of the brain using magnetic fields, potentially unlocking the secrets of high-level brain functions such as cognition, emotion, and motivation.
The team has introduced the world’s first Nano-MIND (Magnetogenetic Interface for NeuroDynamics) technology, allowing for wireless, remote, and precise modulation of specific deep brain neural circuits using magnetism. This cutting-edge research is published in the prestigious journal Nature Nanotechnology.
The human brain, with its intricate network of over 100 billion neurons, holds the key to understanding complex brain functions and identifying the root causes of various brain disorders. The development of Nano-MIND technology opens up new possibilities for advancing brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and enhancing our understanding of the brain’s inner workings.
By selectively activating targeted brain circuits using magnetic fields and magnetized nanoparticles, researchers at the IBS have demonstrated the potential of Nano-MIND technology in modulating emotions, social behaviors, and motivation in animals. This innovative approach allows for precise control of neural activity, offering new insights into brain functions and potential therapeutic applications.
Director Cheon Jinwoo of the Center for Nanomedicine expressed excitement about the technology, stating, “This is the world’s first technology to freely control specific brain regions using magnetic fields. We expect it to revolutionize research in neuroscience, artificial neural networks, brain-computer interfaces, and treatments for neurological disorders.”