A remarkable discovery has been made by an international team of anthropologists in France – a bone found in a cave that may represent a previously unknown lineage of Homo sapiens. This groundbreaking study has been published in the prestigious journal Scientific Reports.
The Grotte du Renne, a cave in France, has been a focal point of archaeological research for many years. Through extensive exploration, it has been revealed that the cave contains layers of historical significance. Deeper layers indicate the time when Neanderthals inhabited the cave, while higher layers represent the period when anatomically modern humans (AMHs) occupied it.
Between these layers lies another layer that suggests a coexistence between the two hominids. Stone tools discovered in this layer have been attributed to an early Châtelperronian techno-cultural complex. However, scholars have not reached a consensus on whether these tools were crafted by Neanderthals, AMHs, or both.
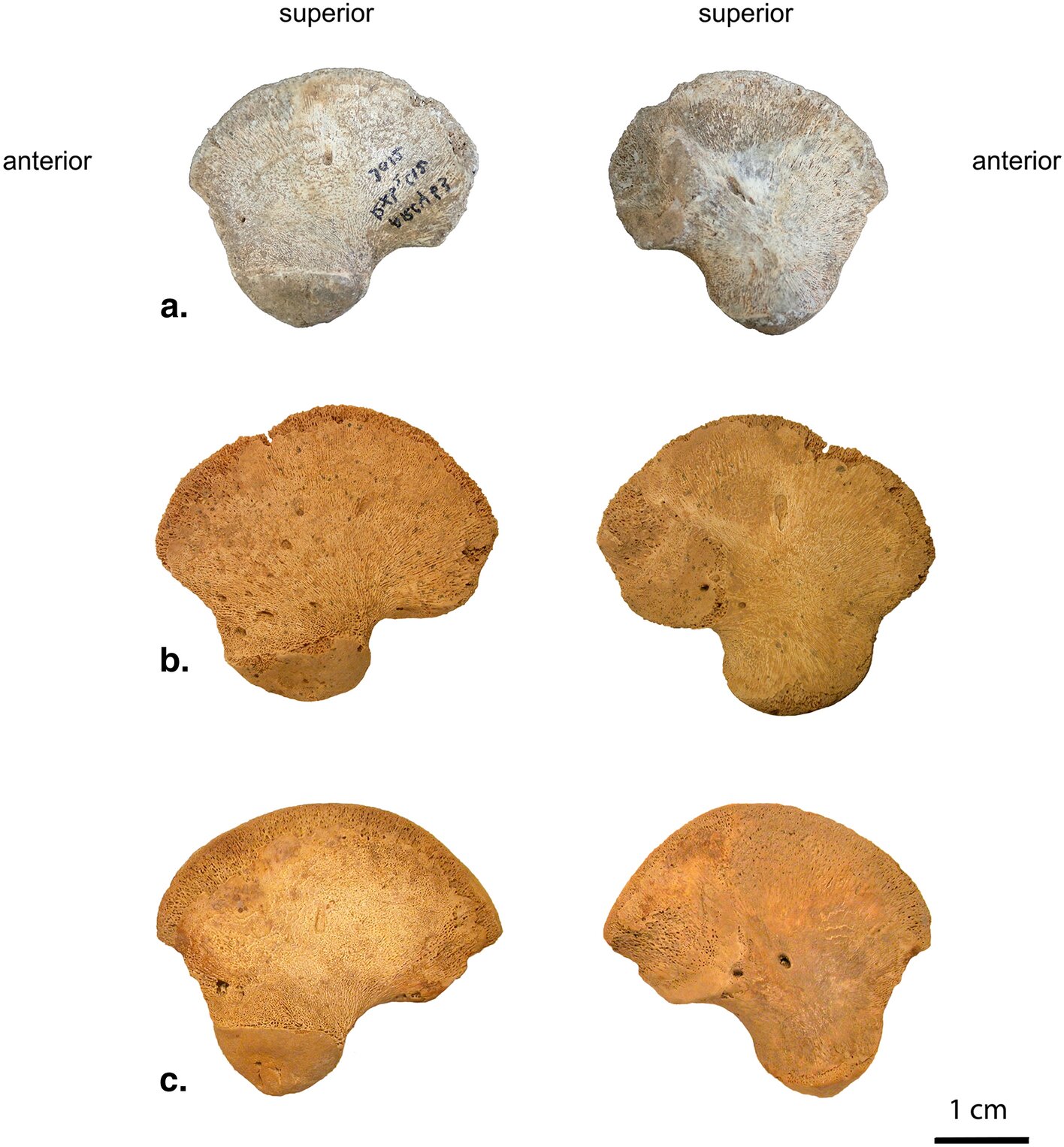
In this groundbreaking study, the research team reexamined a bone excavated from the cave many years ago – an ilium, or hip bone, from a newborn baby. Through meticulous comparison with other Neanderthal and modern baby bones, they determined that it did not belong to either species. Its unique shape deviated from the normal variation observed in humans, leading the researchers to conclude that it represents a previously unknown lineage of Homo sapiens with distinct morphology.
The researchers propose that the tools from the Châtelperronian techno-cultural complex may have resulted from diffusion. According to this theory, AMHs developed the tools, and Neanderthals imitated and adapted them to suit their own needs. This hybridization is believed to have occurred in various parts of Europe during the coexistence of Neanderthals and AMHs.
,,,,