At first glance, the question of the longest-surviving civilization may seem simple, but the answer is far from it. The disagreement among modern historians on key factors used to determine a civilization makes it challenging. Can we even use terms like “civilization” universally? How do we define when a civilization begins and ends? Moreover, considering that many historical civilizations were ruled by foreign powers at certain times, can we consider them as one continuous entity or something else entirely?
The concept of a “civilization” is frustratingly elusive and difficult to apply in a meaningful and comparative way. So, how can we approach this challenge? One approach is to look for evidence of enduring culture and traditions over time. Shifting the focus in this manner provides us with something more tangible. The following examples are considered the longest-lasting cultures in history, but examining their nature reveals why the term “civilization” is so complex.
Ancient and not-so-ancient China
If you ask people which civilization has survived the longest, many would say China, and for good reason. China boasts the world’s oldest written language, which has been used for approximately 6,000 years. Even more astonishingly, characters used today can be found on artifacts like the Oracle bones, which are at least 3,000 years old. No other culture can claim such a remarkable continuity.
However, can we compare modern China to its ancient predecessor, or are they too dissimilar to be considered part of one long civilization? According to a study conducted by the Chinese State Administration of Cultural Heritage, China can indeed be regarded as over 5,000 years old. Yet, not all historians agree. Some argue that this claim holds significant political value in legitimizing contemporary China’s existing structure. Additionally, the vastness of the region and its diverse ethnic groups make it challenging to label them as a homogenous people with the same culture and traditions.
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt is another prominent contender for the title of the oldest-surviving civilization. However, this assessment is also difficult to make.
Egypt was a vast kingdom in the ancient world, first unified around 3100 BCE and lasting until 332 BCE when it was conquered by the Macedonians. Despite this political change, the language remained the same, and hieroglyphics continued to be used until the 5th century CE, 3,500 years after their inception. But does this represent continuity or change?
Similarly, some might consider the ancient Egyptian religion as a marker of its longevity. However, it too evolved over time, along with the people who practiced it, until it was eventually replaced by Christianity in the first century CE.
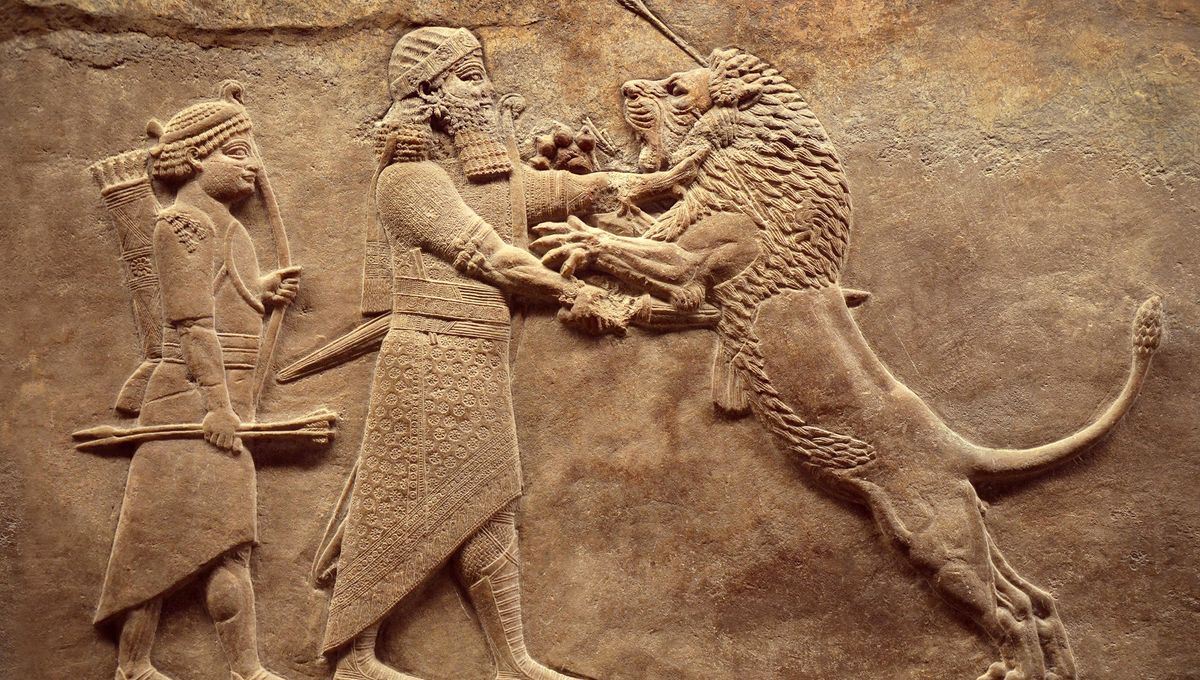
Mesopotamia
The region known as Mesopotamia, based around the Tigris and Euphrates River systems, is considered the cradle of civilization. It witnessed some of the most significant developments in early human history, including the invention of the wheel, sailboats, maps, writing, mathematics, and more.
Humans settled in the region during the Paleolithic era and benefited from the fertile soils created by flooding. Around 12,000 years ago, they utilized this land in what is known as the Agricultural Revolution. Then, approximately 5,000 to 6,000 years ago, the urban revolution began, leading to the formation of larger cities from various villages. The first city, Uruk, dating back to around 3200 BCE, was created by the Sumer people, who are also credited with inventing the first written language.
The history of Mesopotamia is vast and complex, with different rulers and dynasties rising and falling over time. These include the Akkadian Empire, the Gutians, Ur-Namma, the Babylonians, the Hittites, the Assyrians, and the Persian Empire. In 332 BCE, Alexander the Great conquered the region, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.
As a whole, Mesopotamia could be seen as having a history as long as that of Ancient Egypt. However, it is challenging to determine whether this represents one continuous period or a history of changes and different cultures.