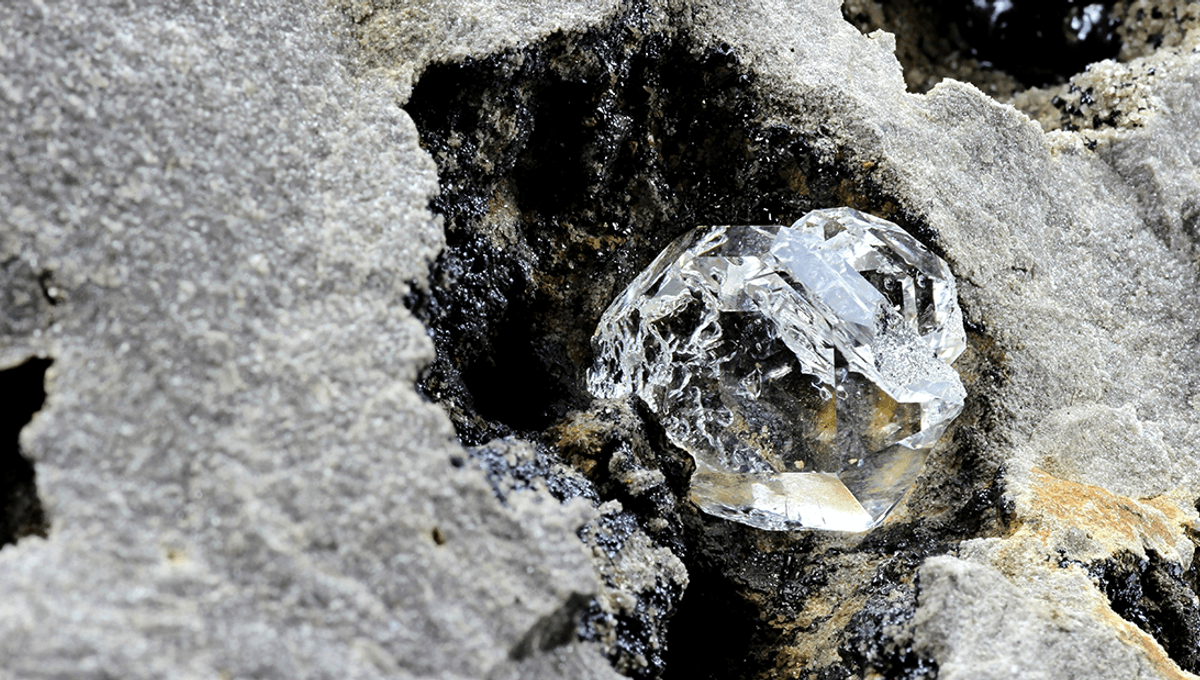
Prepare to be dazzled! A team of brilliant geologists has made an extraordinary breakthrough in the search for diamonds, those coveted and incredibly valuable gemstones. They have discovered a way to pinpoint the exact locations where diamonds, the hardest naturally occurring material known to man, are formed deep within the Earth.
Now, let’s delve into the fascinating world of diamonds. These precious gems can only be created under extreme pressure and scorching temperatures, hidden away in the depths of our planet. Occasionally, they are brought to the surface through volcanic eruptions in a type of molten rock called kimberlite. However, the mystery lies in what triggers this eruption and brings these dazzling treasures to light.
In a recent groundbreaking study, the team explored two competing theories that attempt to explain this phenomenon. One theory suggests that kimberlite magmas exploit the “wounds” created when the Earth’s crust stretches or when tectonic plates split apart. The other theory involves colossal upwellings of molten rock called mantle plumes, which surge up from the core-mantle boundary nearly 2,900 kilometers beneath the Earth’s surface.
Both theories, however, fail to provide a complete explanation of how magma finds its way through the Earth’s crust or the composition of the resulting kimberlite. Undeterred, the team employed statistical analysis and machine learning to investigate the breakup of continents and its connection to kimberlite formation. Their findings revealed that most kimberlite volcanoes erupt 20-30 million years after tectonic breakups.
But here’s the real gem of their discovery: kimberlite eruptions gradually migrate from the edges of continents to their interiors over time, and this migration occurs uniformly across all continents. This crucial clue led the team to develop a computer model that suggests diamond eruptions are triggered by a fascinating “domino effect.” As continents drift apart, rifts of thinned crust form, causing regions of thick, cold rock to sink into the hot magma below. This, in turn, triggers an upwelling of the mantle and similar flows in nearby continents.
Through their computer models, the team demonstrated that this process brings together the necessary ingredients in just the right amounts to generate gas-rich kimberlites. Once formed, the buoyant magma, propelled by carbon dioxide and water, rapidly ascends to the surface, carrying its precious cargo of diamonds.
Not only is this study a captivating exploration of diamond explosions within the Earth’s crust, but it also holds practical implications for locating these coveted gemstones. Furthermore, this groundbreaking research could potentially lead to the discovery of other rare elements using the same methodology.
Prepare to be amazed by the wonders of our planet! The study detailing this remarkable breakthrough can be found in the prestigious journal Nature.