Prepare to be amazed by the unsung heroes of the nervous system: neurons. These remarkable cells form intricate networks that transmit vital information throughout the brain and serve as the backbone of nerve conduction. But they don’t do it alone. Glial cells, the brain’s very own immune system, provide support and maintain the optimal environment for neurons to thrive.
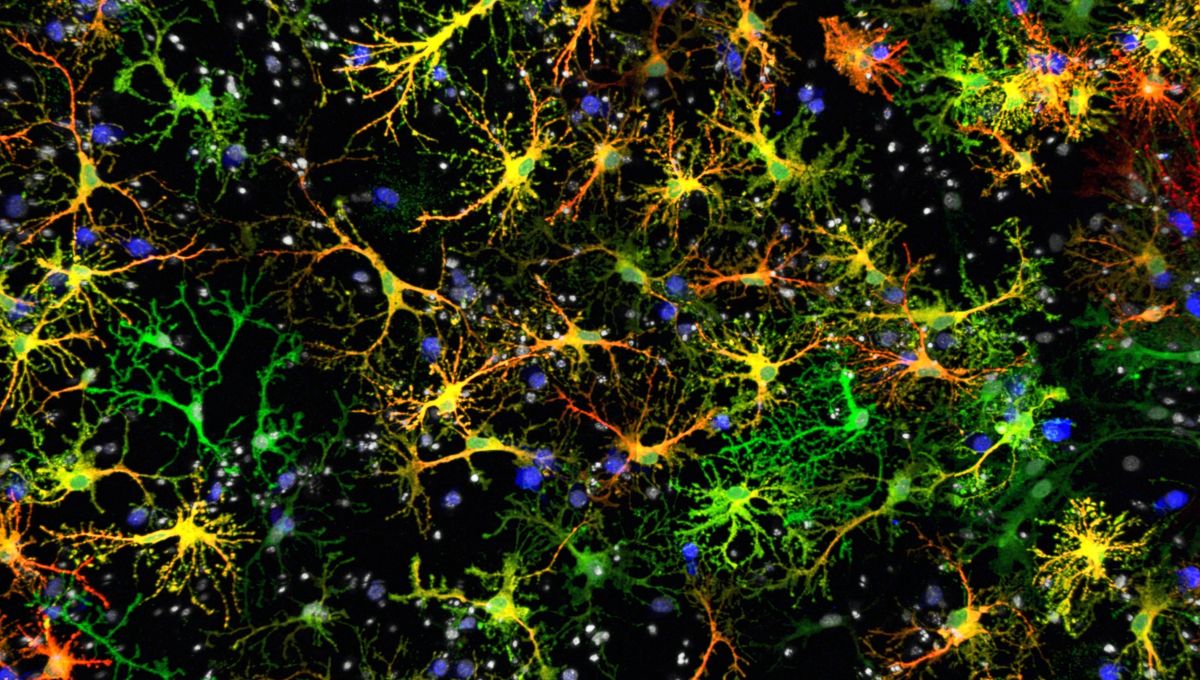
Among the various types of glial cells, there are star-shaped astrocytes that often gather around synapses – the crucial junctions between neurons. These synapses rely on neurotransmitters to bridge the gap and transmit nerve impulses. For years, scientists have speculated about the role of astrocytes in synaptic transmission, but the results have been inconclusive. However, a groundbreaking study has uncovered a surprising revelation.
Using cutting-edge technology, researchers discovered a group of astrocytes equipped with all the necessary machinery for a function typically associated with neuronal synapses. These astrocytes seemed capable of releasing glutamate, the brain’s most abundant neurotransmitter. Initially observed in mouse cells, the study suggests that this function is also present in humans.
But did these astrocytes actually perform their newfound function? Advanced imaging techniques provided the answer. The team witnessed the release of glutamate from specific areas of these cells, mirroring the behavior of synapses in neurons. Even more astonishingly, the released glutamate appeared to impact synaptic transmission and the regulation of neuronal circuitry.
These hybrid cells, as the researchers call them, play a crucial role in modulating neuronal activity and controlling communication and excitation levels among neurons. They even contribute to long-term potentiation, a process essential for memory formation. This discovery opens up exciting possibilities for understanding memory-related disorders like dementia, as well as potential connections to epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
With the emergence of this new type of cell, the scientific community now has a wealth of research opportunities. The team plans to investigate the protective role of these cells in Alzheimer’s disease and explore their involvement in other regions and pathologies beyond the scope of this study.
Prepare to delve into the mysteries of the nervous system as this groundbreaking study, published in Nature, unveils the hidden potential of these hybrid cells.