A team of astronomers from Istanbul University in Turkey has conducted an extensive study on a Galactic open cluster called Collinder 74. Their findings, which were recently published in Physics and Astronomy Reports, provide valuable insights into the properties and characteristics of this cluster.
Open clusters, or OCs, are groups of stars that are loosely bound together by gravity and formed from the same giant molecular cloud. Over 1,000 of these clusters have been discovered in the Milky Way so far, and scientists are eager to find more in order to better understand the formation and evolution of our galaxy.
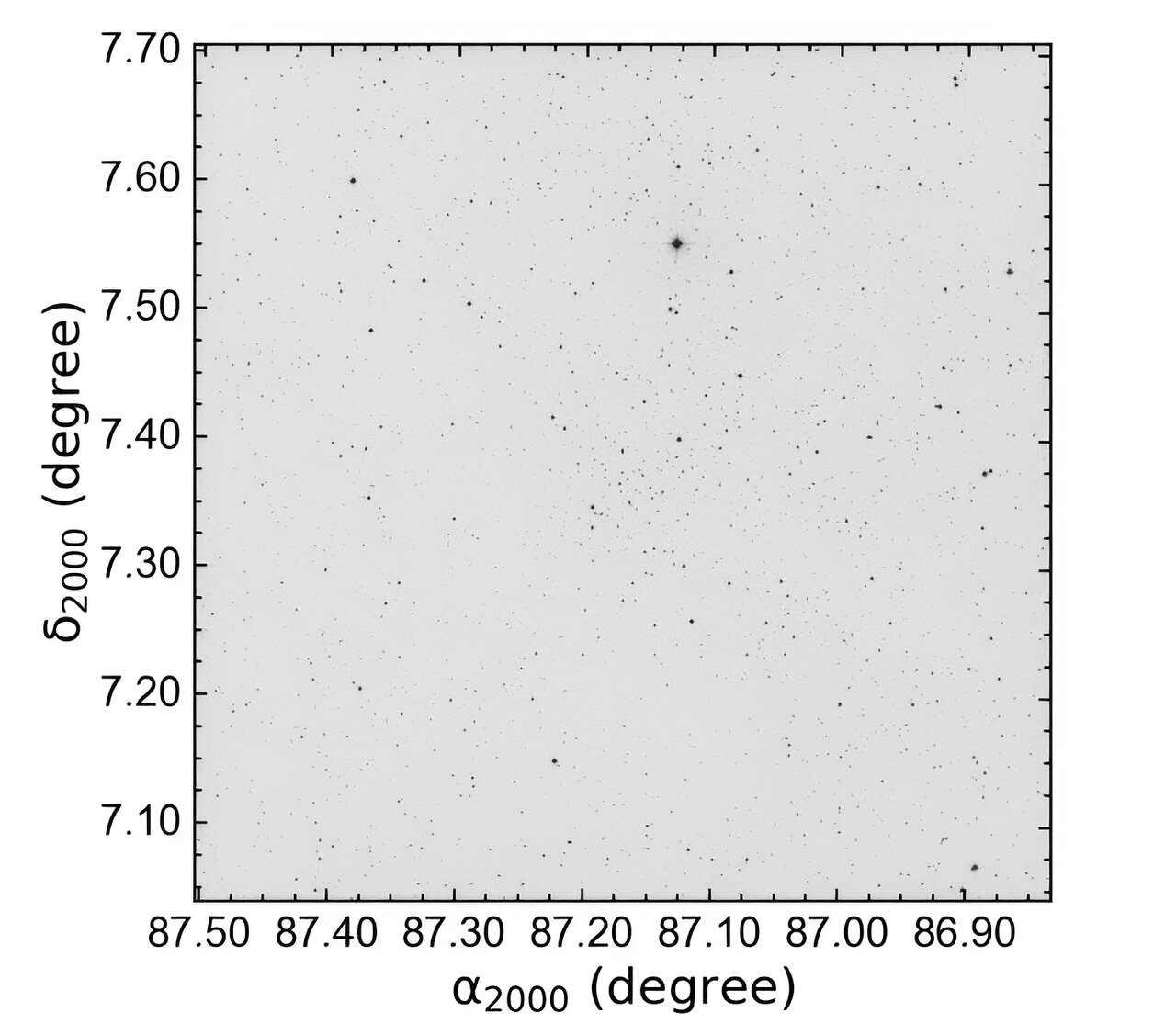
Collinder 74, located approximately 8,000 light years away from Earth, is an intermediate-age open cluster that is centrally concentrated. Previous observations have provided estimates of its metallicity and reddening. However, many parameters of Collinder 74 still remain uncertain.
To address this, astronomers Talar Yontan and Remziye Canbay from Istanbul University utilized data from ESA’s Gaia satellite to investigate the properties of this cluster. They identified 102 member stars within the cluster and used them to determine its structural and fundamental astrophysical parameters.
Additionally, Yontan and Canbay discovered four blue straggler stars among the identified members. These stars exhibit a flat radial distribution, with three of them located at specific radial distances and one located at a different distance.
The study revealed that Collinder 74 has mean proper-motion values in right ascension and declination. Its distance was calculated to be approximately 9,200 light years, and its age was estimated to be 1.8 billion years. The cluster has a radius of 26.9 light years, a total mass of 365 solar masses, and a metallicity level of -0.052. The mass function slope of the cluster was determined to be around 1.34.
In terms of orbital parameters, the researchers found that Collinder 74 has a radial velocity, orbital period, and orbital eccentricity. Based on these findings, they concluded that Collinder 74 is a member of the thin-disk component of the Milky Way galaxy.
This comprehensive study of Collinder 74 provides valuable insights into the nature and properties of this Galactic open cluster. By studying open clusters in detail, scientists can enhance their understanding of the formation and evolution of our galaxy.